

Often shifts from one uncompleted activity to another.Difficulty organizing goal-directed activities.There are some major differences between ADD and ADHD: ADHD, has symptoms such as fidgeting, being constantly in motion, restlessness, talking excessively, blurting out answers, and interrupting others. Tendency to lose things necessary for tasks or activities Both are considered to be a type of the same condition.Often does not seem to listen to what is being said.Often difficulty following through on instructions from others.Often easily distracted by extraneous stimuli.ADD (Attention Deficit Disorder) with or without hyperactivity is the older term from the DSM-IIIR.Ĭommon symptoms of ADHD (inattentive type):
#DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ADD AND ADHD MANUAL#
However, the updated term, according to the DSM IV, is ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder).Īttention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is the term used in the current Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) diagnostic criteria. They don’t draw the negative attention to themselves as do those with Classic ADD.The terms ADD and ADHD have been used interchangeably. Inattentive ADD is common but is often missed because children with this type tend to have fewer behavioral problems. They may be labeled as unmotivated-even slow or lazy. Those suffering with this type are usually quiet, more introverted, and appear to daydream a lot.
Inattentive ADD is the second most common type of ADD. The latter are structures deep in the brain that produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is critical for motivation, attention, and setting the body’s idle speed.

Symptoms of ADHD include inattention (not.

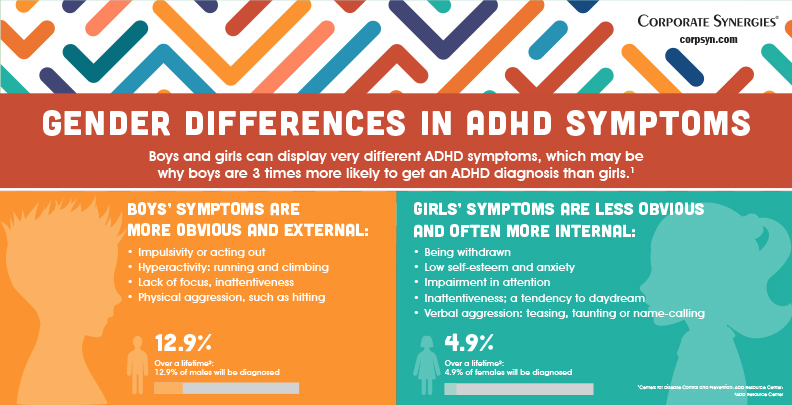
Making careless mistakes/poor attention to detailĬlassic ADD SPECT scan findings often show normal activity at rest, but during concentration there tends to be decreased activity in the underside of the prefrontal cortex as well as in the cerebellum and basal ganglia. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common mental disorders affecting children.Trouble listening when others talk to them.Even as adults, those with this type of ADD tend to have a great deal of energy and a preference for physical activity rather than a more sedentary lifestyle. Classic ADD tends to be more frequently seen in boys. When inattention is combined with significantly heightened activity level and impulsiveness, ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) may be a more. Parents of these kids are often tired, overwhelmed, and even embarrassed by the behavior of their non-stop and hard-to-control children. At Amen Clinics, we do not use the term ADHD exclusively because not all the ADD types are hyperactive. Classic ADD is often called ADHD, with an emphasis on the hyperactive behavior trait. Their hyperactivity and conflict-driven behavior gets everyone’s attention early on. As children, they tend to be restless, noisy, talkative, impulsive, and demanding. As babies, they tend to be colicky, active, and wiggly. This first type of ADD is usually evident early in life. A short attention span for everyday tasks (e.g.Another study has found that children with untreated ADD/ADHD are nearly twice as likely to develop an alcohol use disorder or other substance abuse problem, and that they tend to start using at an earlier age compared to other kids. Statistics show that 33% of kids with ADD/ADHD never finish high school (3 times the national average) so they end up in jobs that don’t pay well. This condition is often overlooked in females because their primary issue is inattention, and they are less likely to exhibit the disruptive hyperactivity that is so often seen in males with ADHD. In fact, the National Institute of Mental Health has found that 5.4% of adult men and 3.2% of adult women have ADD/ADHD, and other research has shown that only about 20% of them have ever been diagnosed or received treatment. While the symptoms of ADD/ADHD emerge in childhood, if left untreated, they can persist throughout a person’s life. To further complicate things, it is not uncommon for a child with this condition to also have a learning disorder, thus adding to the academic challenges they face. Hormone Evaluation and Replacement TherapyĪccording to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), 9.4% of children between the ages of 2 and 17 have been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD.Marital Conflict and Relationship Issues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
